The Endocannabinoid System
Our body is continuously in a state of flux, reacting to internal and external stimuli to maintain a state of balance, otherwise known as homeostasis. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is in charge of maintaining this state of equilibrium.
While historically scientists hypothesized the brain was in charge of regulating and overseeing our body, it’s now clear that this falls within the remit of the ECS.
The ECS
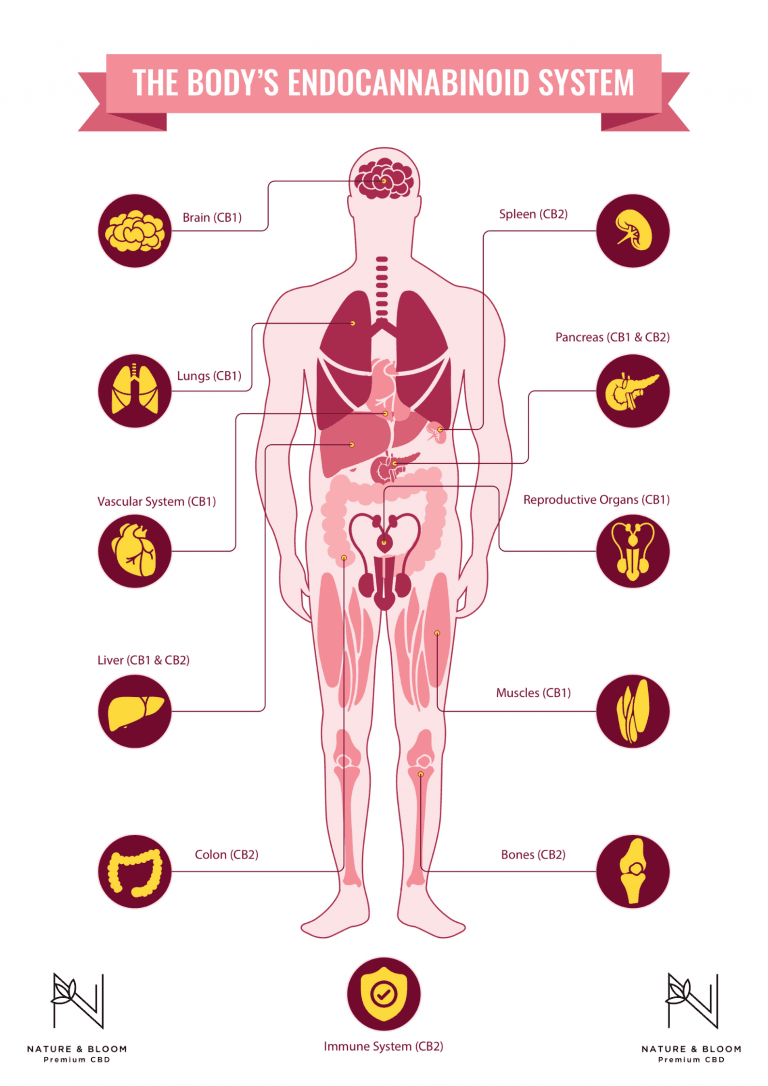
This system is found in all animals except insects, and it’s known to be over 600 million years old. The ECS consists of 2 receptors called CB1 and CB2. Both of these control activities downstream and can be thought of as a switchboard that acts and reacts to regulate and overall maintain our health.
Critical systems such as the central nervous, endocrine, and digestive system are all interwoven with ECS receptors and which respond to its direct instruction via the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Interestingly, cannabis compounds known as cannabinoids act as essential agents to the functioning of this system. More so, our body produces our own (endo)cannabinoids, which are essentially mimicked by those found in Cannabis.
Here by Design
It’s one of the primary reasons why Cannabis is able to yield such a broad set of effects while maintaining a high level of relative safety. Furthermore, research into the ECS has outlined that the consumption of plant-derived cannabinoids can help support our bodily functions and keep them running optimally.
Further Study
It’s more than likely that we currently only see the tip of the iceberg. Our understanding of the ECS and cannabinoids still requires much more work. However, given the pace research is moving, there is no doubt we will discover some more compelling use cases for this system in time.